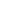
Hemorrhoids are divided into 4 stages:
Stage I: The hemorrhoidal bulb is very small, cannot be felt, does not protrude, and may bleed.
Stage II: The hemorrhoidal bulb comes out with straining, and goes back in by itself when defecation is completed. It may bleed.
Stage III: The hemorrhoidal bulb comes out with straining and can only be pushed back in by hand.
Stage IV: The hemorrhoidal bulbs are always out, cannot be pushed back in by hand, and require surgical intervention.
Diagnosis: It is diagnosed with ano-rectal examination, colonoscopy, rectoscopy.
Treatment: To protect against hemorrhoids, plenty of water should be drunk, exercise should be done, constipation should be avoided, and the diet should focus on whole grain, vegetable, and fibrous foods.
Drug therapy: Painkiller pomades, steroid pomades, anti-constipation and stool softening drugs, and drugs that regulate blood flow in this area are used.
Band ligation: The hemorrhoid lump is pulled with a forceps and a rubber band is placed at its base. In this way, the hemorrhoid lump is allowed to decay and break off.
Sclerotherapy: A special drug is injected into the base of the hemorrhoid lump to provide adhesion and shrink the lump.
Laser, infrared, cryotherapy, and suturing the base of the lump are other treatment methods.
Surgical treatment: It is applied to III. and IV. degree hemorrhoids. The most commonly used method is open and closed Milligan-Morgan Hemorrhoidectomy. In these methods, the hemorrhoid lumps are surgically removed.